two-part study on calcium removal in drinking water
- info7643583
- 17 jun 2025
- 1 minuten om te lezen
Today, our two-part study on calcium removal in drinking water treatment has been officially published as open access in Water Research journal. The result of collaboration between Waternet, Utrecht University, Delft University of Technology and Queen Mary University of London.
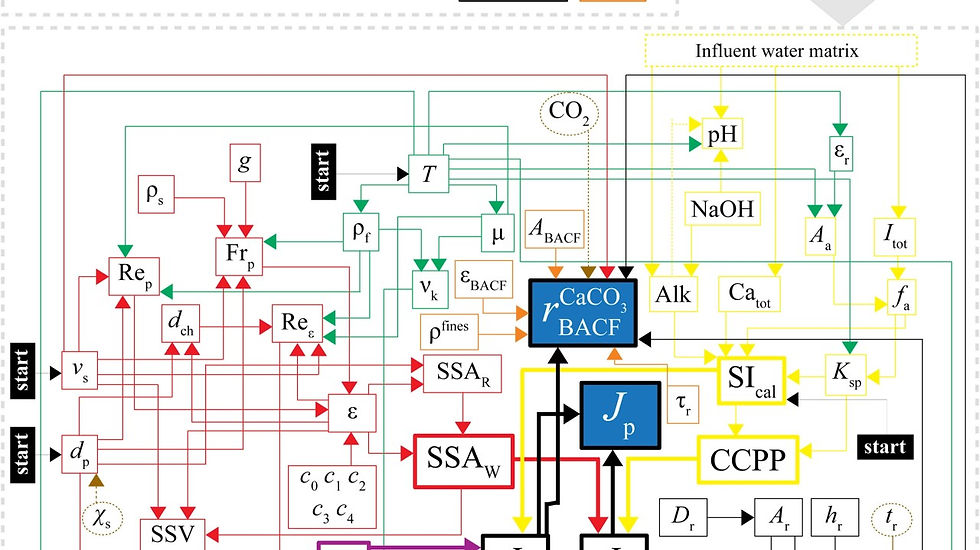
Pellet softening is widely used, but current models often consider only part of the process or rely on simplified assumptions. Our work provides a new perspective.
The first article introduces a mechanistic model that describes both crystallisation on pellets and nucleation in the water phase. It uses explicit, physically grounded formulas based on key process variables such as flow velocity, temperature, particle size and saturation.
The second article applies and tests the model in laboratory, pilot and full-scale reactors. It shows how mixing conditions and water composition influence both calcium removal and the formation of fines, which can affect downstream steps like activated carbon filtration.
By linking reactor behaviour to downstream impact, the model supports more robust operation, improved design and better long-term performance of softening systems.

Part 1 – model and design strategy:
Part 2 – operational control and validation:
Warm thanks to the Waternet team managing the pilot installation, to lead researcher Sergěj Seepma, and to Professor Mariette Wolthers for her scientific guidance throughout.
hashtag#water hashtag#pelletsoftening hashtag#drinkingwater hashtag#waterresearch hashtag#reactormodelling hashtag#processdesign hashtag#sustainability hashtag#education hashtag#research hashtag#reactordesign hashtag#integratedwatertreatment hashtag#waterquality hashtag#futureproof hashtag#fluidisedbed


Opmerkingen